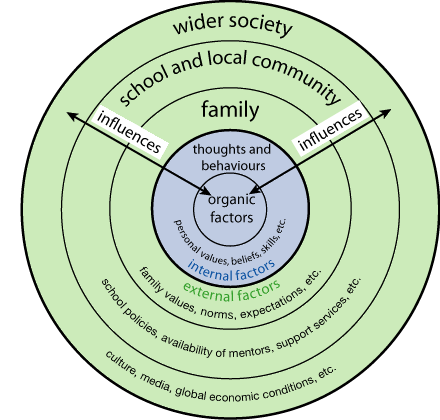
What is the Ecological approach to classroom management?
The ecological approach is viewing and teaching to the individual. It is the realization that everyone is unique. It is building a person and having an impact on their development within a community. It is a journey that leads to responsibilities, morals, and participation within a society. A teacher must be aware of individual development in order to respond to and facilitate their learning.
Responsibilty and Viewing the Individual- A Short Essay
Responsibility and Viewing the Individual
There is a problem that occurs when viewing teaching as strictly a service or profession. The problem occurs when we view schools as factories or businesses, or when we forget that what makes up the majority of the schools are individuals. Instead of this view, we need to focus on the individual and what makes them unique. As professionals we need to learn to ask ourselves: what is it that will motivate a child to learn to not only improve themselves, but society. When we focus on a profession, we forget the people that we are serving.
We need to turn our focus to the individuals. “Exploring human nature, understanding the dynamics of teaching and learning, working beyond our current tools for quantifying human qualities may be intricate work…, but we are at a critical mass and moving forward” (Ellsworth, 2001). Shifting learning onto the shoulders of our students has become a way for them to hold a certain amount of responsibility in what and how they learn. In essence, this will teach them how to work with a community of learners and in communities outside the school building. “The child is already a master at learning, but has little experience learning with rigor in the milieu of community” (Ellsworth, 2001). Increasing student responsibility has lead to teachers to become facilitators in the classroom. Instead of producing and reproducing information for the students, it should be our job to facilitate the learning in the classroom.
Facilitating classroom instruction is only one role a teacher takes to increase student responsibility. As a team builder and a builder of community, the teacher can model how to utilize individual strengths and personalities that best suit the community of learners or the content area that is being explored. It may be a difficult process to start. However, it has become necessary as we find that students require these skills as they move on within our society. Developing the individual instead of a factory built repetition machine has become important in today’s world. With that said, we find ourselves looking toward authentic activities that can incorporate the knowledge and content area deemed necessary for survival outside of our schools. These activities should incorporate guided practice and responsibility that our students will need once they leave the school environment.
References:
Ellsworth, J. (2001). Teaching and learning: Embracing a new vision. Classroom Management
of Exceptional Children. Retrieved from http://jan.ucc.nau.edu/~jde7/ese425/eco/online_read_1.html.
Process Lesson Plan
Product Overlay - Science: Plant Structures
Grade Level: 3
Time Needed: 45 minutes
Annotated List of Materials:
· Tissue Paper
· Rulers
· Pencils
· Scissors
· Green Pipe Cleaners
· Clear Tape
· Green Florist Tape
· Dried Grass (Symbolize Roots)
· Flower Structure Worksheet
· Paper
Type of Lesson: Whole Group
Connection to Standards:
Strand 4: Life Science
Concept 1: Characteristics of organisms
Understand the relationships among various organisms and their environment.
PO 1. Describe function of the following plant structures:
Roots - Absorb nutrients
Stems - Provide support
Leaves – Synthesize food
Flowers – Attract pollinators and produce seeds for reproduction
Instructional Objective: All students will describe the function of the four given plant structures by creating a flower and labeling its structures and functions with 90% accuracy.
Accommodations/Modifications: Students who require extra time will be paired with students to assist them. Picture dictionaries will also be provided for those who have trouble with the vocabulary. Those who have increased difficulty will have extra assistance from the teacher.
Lesson Sequence:
Introduction/anticipatory set
1) Bring in a potted flower to show to the students.
2) Ask: Can anyone tell me why a plant has a stem? What would happen if a plant did not have a stem?
Modeling
3) The teacher should go over the parts of a flower and discuss them with the class. Using a vocabulary graphic organizer, identify, label, and describe the function of each part of the flower.
Checking for Understanding
4) Have the students quickly quiz learning partners about the parts of a plant.
Guided Practice
5) Pass out the materials needed to make the flower.
6) As a class go step-by-step and make the flower. Ask students to identify the parts of the flower as they are made
Independent Practice
7) Using the plant structure worksheet, have the students individually fill in the plant structures and provide the definitions. If students finish early, allow them to read books about plants.
Closure
8) When students are done, collect supplies and clean up.
9) As students are cleaning up the materials, again point out the parts of the flower and have the students identify them and describe their function.
Assessment: Students will describe the function of the four given plant structures by completing a flower graphic organizer and labeling its structures and functions with 90% accuracy.
Extensions: Students can do further research on plant structures and share any interesting insights with the class. Students can also use the vocabulary terms to develop one-paragraph stories about their flowers. The stories can be shared with the class.
Lesson Plan – Process Overlay
Process objectives – Flower creation
Share materials to create flower
Follow directions to complete the flower
Clean-up after flower is created
Possible Thematic Goals Proper use of materials, Respect for the Earth and its living things, Plant life, Listening skills
Materials – Directions for flower making in simple kid-friendly terms
Sample procedures: Pass out and review procedural guidelines:
Proper use of Materials
Sharing materials with others
Clean-up procedures after craft activity is complete
Choose and review consequences
Process List
Material Usage: 1) use for intended purpose; 2) follow directions in making the flower carefully; 3) return to proper place when finished
Material Sharing: 1) Take one material at a time; 2) return materials to proper place before getting another; 3) if limited quantities of the materials are available, and another asks to use the tool, be prepared to share materials and use for a reasonable length of time; 4) student should be willing to let another student use the material if they are planning to use it for an extended amount of time.
Consequences of failure to observe procedures and guidelines: 1) First time violation - orally review rules; 2) Second violation within short space of time - limit use of available materials to those used correctly; 3) if repeated failure to use materials correctly lose opportunity to make flower with craft materials; 4) possible solution is to draw flower on paper
Student Monitoring Sheet
| Product |
| ||||||||
|
| Language Arts | Science | Math | Social Studies | Reading |
| |||
| Monday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Tuesday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Wednesday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Thursday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Friday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Process |
| ||||||||
|
| Language Arts | Science | Math | Social Studies | Reading |
| |||
| Monday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Tuesday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Wednesday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Thursday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Friday |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Key |
| ||||||||
| Tool use = T Sharing = Sh Kindness = K Creative = C | Stewardship =Sw Honest = H Expressive = E Empathic = Em | Reflective listening= Rl Good partner = GP Communicate = C Encouraging = En | Cooperative = Co Stewardship = St Share self = Ss Persevere = Pp | ||||||
| Team member = Tm Follow rules = FR Helpful = He Hard work = HW | Self control = SC On time = Ti Honor student =HB Respectful = R | Orderly = O Pride in work = P Friendly = F Do favor = Df | Morale is high = M Extra Effort = EE On time = OnT On task = OTa | ||||||
Concluding remarks about the ecological model

The ecological model looks at students as individuals and recognizes their uniqueness. It shifts responsibility to the students for their learning and asks that teachers learn to utilize individual strengths and recognize human growth as an important aspect to learning. Teachers need to take on the role of facilitators instead of givers of information. Students learn by becoming responsible and taking action in their learning.